Doctor Web offers help to users whose systems have been compromised by an archive-blocker Trojan
Real-time threat news | All the news | Virus alerts
August 1, 2012
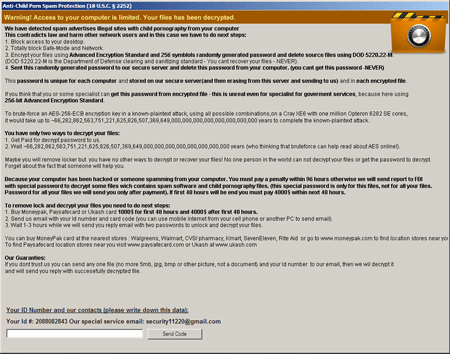
Trojan.ArchiveLock.2 is written in PureBasic. Once the Trojan has penetrated a system, it will paralyse its operation and display a message showing the criminals' demands.
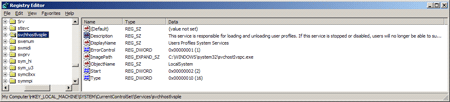
Then the Trojan places an encryption application into a system folder. When launched with the install or i option, the encryption program is installed as a system service. Different versions of the Trojan use different file names and descriptions for the service.
When launched as a system service, the encryption module creates a large number of files, some of which are used to store configuration data, paths to configuration files, logs and executables, as well as information about the infected computer. In particular, it saves information about the OS version, locale, titles of windows opened by running applications, the Windows boot mode ( or SafeMode), and then clears the Recycle Bin and compiles a list of encrypted and deleted files. First Trojan.ArchiveLock.2 deletes files that appear as backups. Then the Trojan uses a special routine to generate a list of passwords and launches WinRAR to place files on the compiled list into password-protected SFX archives. Trojan.ArchiveLock.2 can encrypt more than 100 file types. The original files are deleted with Sysinternals SDelete by repeated overwriting, which makes restoring the removed objects impossible. Some archives are protected by a weak password generated using the hard-disk serial number; for others a special password whose length may exceed 50 characters is used. The names of encrypted files are also changed according to a certain pattern; for example, an archive containing the graphics file picture.jpg will have the following name: picture.jpg(!! to decrypt email id 12345678 to sec****@gmail.com !!).exe.
Trojan.ArchiveLock.2 also features a decryption module that restores previously compressed files if the user enters a correct password.
The malware signatures are present in the databases of Dr.Web anti-virus software, so Trojan.ArchiveLock.2 is not dangerous for computers running Dr.Web Anti-virus or Dr.Web Security Space. However, Doctor Web's analysts have created a special procedure that can—with a high degree of probability—recover files encrypted by the Trojan. If your files have been compromised by Trojan.ArchiveLock.2, please submit a ticket in the Request for Curing category. Do not delete files or reinstall the OS—such actions can make decryption of the files impossible.