Hidden cryptocurrency mining and theft campaign affected over 28,000 users
Real-time threat news | Hot news | All the news | Virus alerts
October 8, 2024
During routine analysis of cloud telemetry submitted by our users, specialists at the Doctor Web virus lab detected suspicious activity of a program disguised as a Windows component (StartMenuExperienceHost.exe, a legitimate process with this name is responsible for managing the Start menu). This program communicated with a remote network host and waited for an incoming connection to immediately launch the cmd.exe command line interpreter.
Disguised as a system component was the Ncat network utility, which, when used for legitimate purposes, transfers data over the network via the command line. This discovery helped reconstruct a sequence of security events, including attempts to infect computers with malware, which were prevented by Dr.Web.
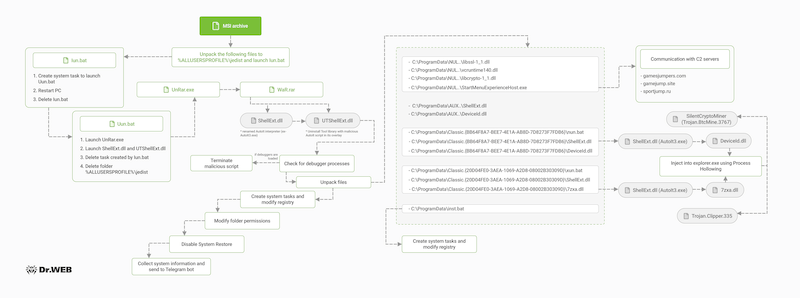
The source of infection is fraudulent pages created by attackers on GitHub (note that such activity is prohibited by the platform's rules) or Youtube pages containing malware links in the description below the video. By clicking on the link, the victim downloads a self-extracting, password-protected archive. Because the archive is encrypted, it cannot be automatically scanned by antivirus software. After entering the password provided by the hackers on the download page, the following temporary files are extracted to the %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\jedist folder on the victim's computer:
- UnRar.exe - an application for extracting RAR archives;
- WaR.rar - a RAR archive;
- Iun.bat - a script that creates a task to run the Uun.bat script, then initiates a computer restart, and deletes itself;
- Uun.bat - an obfuscated script that extracts WaR.rar, runs the ShellExt.dll and UTShellExt.dll files it contains, and then deletes the task created by Iun.bat and the jedist folder along with its contents.
The ShellExt.dll file is an AutoIt language interpreter and is not malicious in and of itself. However, this is not its true name. Attackers have renamed it from AutoIt3.exe to ShellExt.dll to disguise it as a WinRAR library that is responsible for integrating archiver functionality to the Windows right-click menu. Once launched, the interpreter in turn loads the UTShellExt.dll file, which the cybercriminals borrowed from the Uninstall Tool utility. Perfectly legitimate in its own right, it even carries a valid digital signature, but it has a malicious AutoIt script attached to it. Once executed, the script unpacks its payload, which consists of a series of heavily obfuscated files.
AutoIt is a programming language for creating automation scripts and utilities for Windows. Its ease of use and broad functionality have made it popular with various categories of users, including malware writers. Some antivirus programs detect all compiled AutoIt scripts as malicious.
The UTShellExt.dll file performs the following actions:
- Scans the process list for running debugging software. The script contains the names of about 50 different debugging utilities, and if at least one process from this list is detected, the script will terminate
- If no debugging software is found, the files needed to continue the attack are extracted on the compromised system. Some of the files are “clean”, they are necessary to implement network communication, while the rest perform malicious actions
- Creates system events to gain network access using Ncat and execute BAT and DLL files, and modifies the registry to gain persistence using the IFEO technique
Image File Execution Options (IFEO) is a feature that Windows makes available to software developers. For example, it allows them to automatically launch a debugger when an application starts. However, attackers can use the IFEO technique to gain a foothold in the system. They accomplish this by swapping the path to the debugger with the path to the malicious file, so that every time a legitimate application is launched, the malicious application is started as well. In this case, the hackers "hijacked" Windows system services, as well as the Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge update processes (MoUsoCoreWorker.exe, svchost.exe, TrustedInstaller.exe, GoogleUpdate.exe and MicrosoftEdgeUpdate.exe).
- Revokes the delete and modify permissions for the folders and files created in step 2.
- Disables the Windows Recovery Service
- Sends the specifications of the compromised computer, its name, operating system version and information about the installed antivirus software to the attackers using a Telegram bot.
The DeviceId.dll and 7zxa.dll files perform hidden cryptomining and cryptostealing functions, respectively. Both files inject their payload into the explorer.exe (Windows Explorer) process using the Process Hollowing technique. The first file is a legitimate library distributed as part of the .NET framework that has a malicious AutoIt script embedded that executes the SilentCryptoMiner miner. This miner has extensive configuration and stealth capabilities for cryptocurrency mining, as well as remote control functionality.
The 7zxa.dll library, which again is a legitimate library of the 7-Zip archiver, contains a clipper. This type of malware is used to monitor data in the clipboard, which it can either spoof or pass on to attackers. In this case, the clipper waits for typical strings in the clipboard that are characteristic of wallet addresses and replaces them with those specified by the attackers. At the time of publication, it is confirmed that only thanks to the clipper hackers were able to get hold of more than 6000 dollars worth of cryptocurrency.
The Process Hollowing technique consists of running a trusted process in a suspended state, overwriting its code in memory with malicious code, and then resuming the process execution. The use of this technique results in the presence of copies of the process with the same name, so in our case three explorer.exe processes were observed on the victims' machines, which is suspicious in itself as this process normally exists as a single copy.
In total, this malware campaign has affected more than 28,000 people, the vast majority of whom are residents of Russia. Significant numbers of infections have also been observed in Belarus, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Ukraine, Kyrgyzstan and Turkey. Since the victims' computers were compromised by installing pirated versions of popular programs, the main recommendations to prevent such incidents include downloading software from official sources, using their open source replacements, and installing capable antivirus software. Users of Dr.Web products are not affected by this threat.
Read more about Trojan.AutoIt.1443