Do shoot the messenger: Telegram-controlled backdoor trojan targets Linux servers
Real-time threat news | Hot news | All the news
July 4, 2024
This malware belongs to the Remote Access Trojan type, better known by its rather unpleasant but very apt acronym — RAT. Essentially, RATs are the same remote access and administration tools we have all become accustomed to since the COVID lockdowns, only this time they are playing for the bad guys. The main difference is that the targeted user should not suspect that someone else is controlling their machine.
The TgRat trojan was originally discovered in 2022. It was a small trojan written for Windows and designed to exfiltrate data from a compromised machine. Not long ago virus analysts at Doctor Web discovered its Linux version.
Our virus lab received a ticket from a hosting provider to investigate an information security incident involving what turned out to be the Linux version of the TgRat trojan. Dr.Web antivirus detected a suspicious file on the server of one of the clients. The file in question was a trojan dropper, i.e., a program designed to deliver malware to an attacked computer. This dropper unpacked the Linux.BackDoor.TgRat.2 trojan into the system.
The trojan is designed to target specific computers: when it starts, it checks the hash of the computer name against an embedded string. If the values do not match, TgRat terminates its process. Otherwise, it connects to the network and implements a rather unusual method for interacting with its control server, which happens to be a Telegram bot.
Telegram is widely used as a corporate messenger in many companies. Therefore, it is not surprising that threat actors can use it as a vector to deliver malware and steal confidential information: the popularity of the program and the routine traffic to Telegram’s servers make it easy to disguise malware on a compromised network.
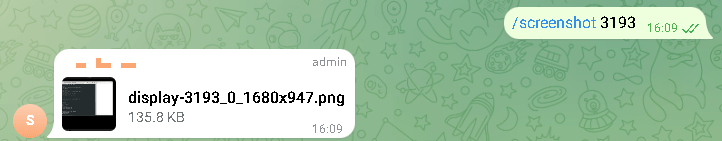
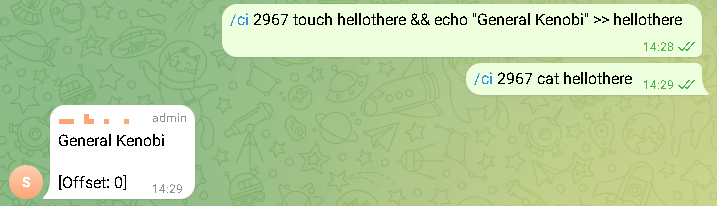
The trojan is controlled through a private Telegram group to which the bot is connected. Using the messenger, attackers can issue commands to the trojan. It can download files from a compromised system, take a screenshot, remotely execute a command, or upload a file as an attachment.
Unlike its Windows counterpart, this trojan was encrypted with RSA and used the bash interpreter to execute commands, allowing entire scripts to be executed within a single message. Each instance of the trojan had a unique identifier, allowing attackers to send commands to multiple bots, connecting them all to a single chat room.
This attack, although unusual in the choice of interaction between the trojan and the control server, can be detected by carefully analysing network traffic: exchanging data with Telegram’s servers may be typical for user machines, but not for a local network server.
To prevent infection, we recommend installing anti-virus software on all local network nodes. Dr.Web Security Suite anti-virus solutions for Windows, macOS, Android, Linux and FreeBSD servers and workstations reliably protect our corporate clients. Additionally, for edge devices at the network perimeter, Doctor Web offers a solution based on Stream Engine scanning technology, which allows traffic data to be scanned for threats with virtually no delay.