Doctor Web’s June 2023 virus activity review
September 6, 2023
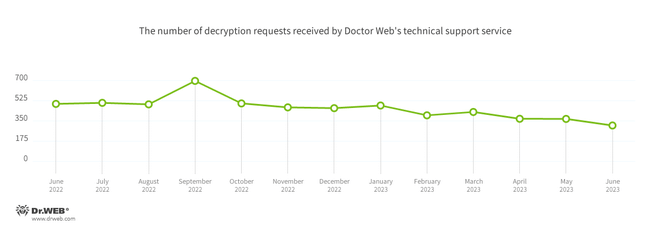
The number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoder trojans decreased by 15.57%, compared to the previous month. The most common encoders were Trojan.Encoder.26996, Trojan.Encoder.3953, and Trojan.Encoder.34027.
Over the course of June, Doctor Web’s malware analysts discovered other fraudulent applications from the Android.FakeApp family on Google Play. In addition, malicious actors again distributed Android.Joker trojan apps that subscribe Android device users to paid services.
Principal trends in June
- A decrease in the total number of detected threats
- Phishing documents were most often detected in malicious email traffic
- A decrease in the number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoder trojans
- The emergence of new malicious programs on Google Play
According to Doctor Web’s statistics service
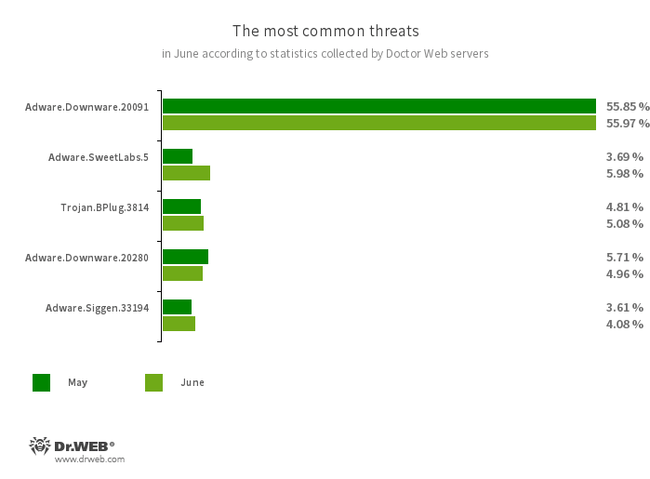
The most common threats in June:
- Adware.Downware.20091
- Adware.Downware.20280
- Adware that often serves as an intermediary installer of pirated software.
- Trojan.BPlug.3814
- The detection name for a malicious component of the WinSafe browser extension. This component is a JavaScript file that displays intrusive ads in browsers.
- Adware.Siggen.33194
- The detection name for a freeware browser that was created with an Electron framework and has a built-in adware component. This browser is distributed via various websites and loaded onto users’ computers when they try downloading torrent files.
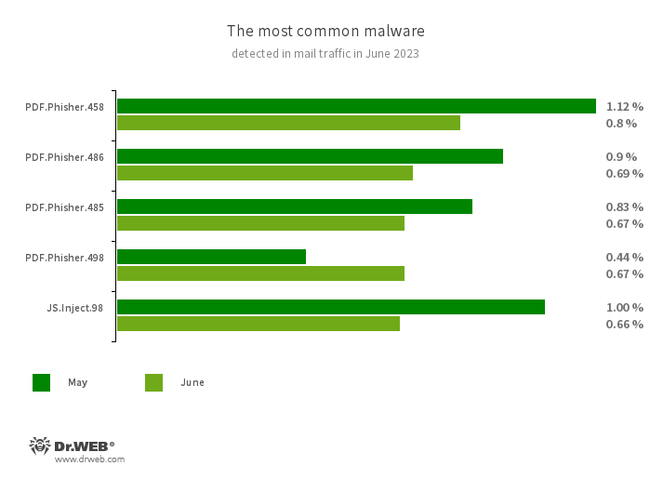
Statistics for malware discovered in email traffic
- PDF.Phisher.458
- PDF.Phisher.486
- PDF.Phisher.485
- PDF.Phisher.498
- PDF documents used in phishing newsletters.
- JS.Inject
- A family of malicious JavaScripts that inject a malicious script into the HTML code of webpages.
Encryption ransomware
In June, the number of requests to decrypt files affected by encoder trojans decreased by 15.57%, compared to May.
The most common encoders of June:
- Trojan.Encoder.26996 — 20.56%
- Trojan.Encoder.3953 — 14.49%
- Trojan.Encoder.34027 — 4.21%
- Trojan.Encoder.35534 — 3.74%
- Trojan.Encoder.37400 — 3.74%
Dangerous websites
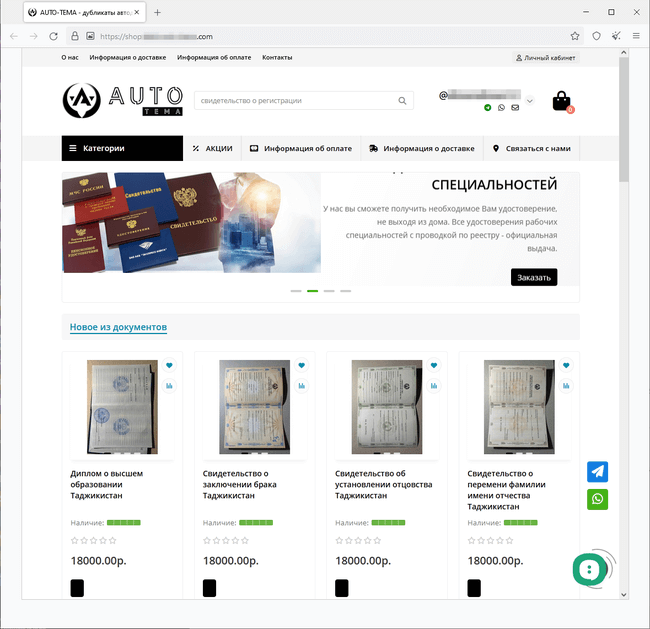
In June, Doctor Web’s Internet analysts observed an increase in the number of websites through which users allegedly can legally purchase or restore certain documents of the Russian Federation, The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), and other countries. Among them, for example, are passports, driver licenses, diplomas, various certificates, and so on. Those who operate these sites assure potential customers of the complete legality and safety of such services. At the same time, they also may note that they are not responsible for the “product” on offer and that all the information on their web resources is presented for “informational purposes”.
Users who resort to such dubious services incur risks for a number of reasons. Not only can they fall victim to fraudsters, who will steal their money, but they can also commit a crime by purchasing a fake document that has nothing to do with the legal one.
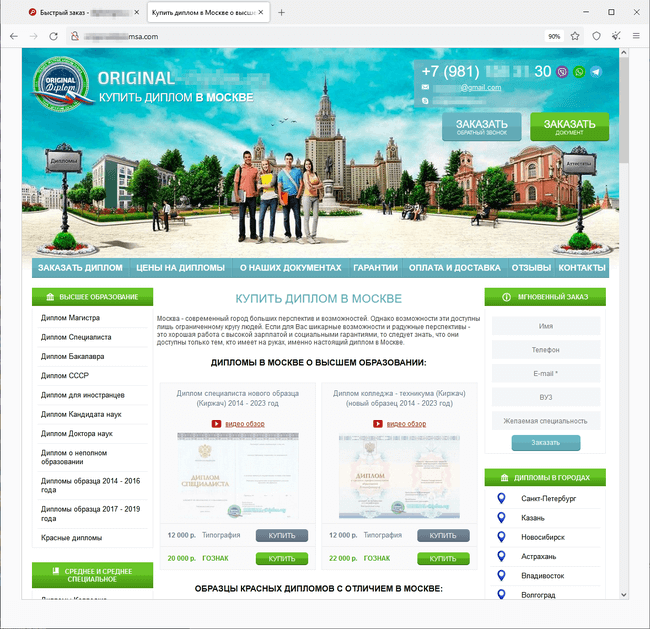
Below is an example of a website that offers the opportunity to purchase the passport of a citizen of the Russian Federation:
Examples of sites that sell higher education diplomas:
An example of a site that offers driver licenses and other documents for purchase:
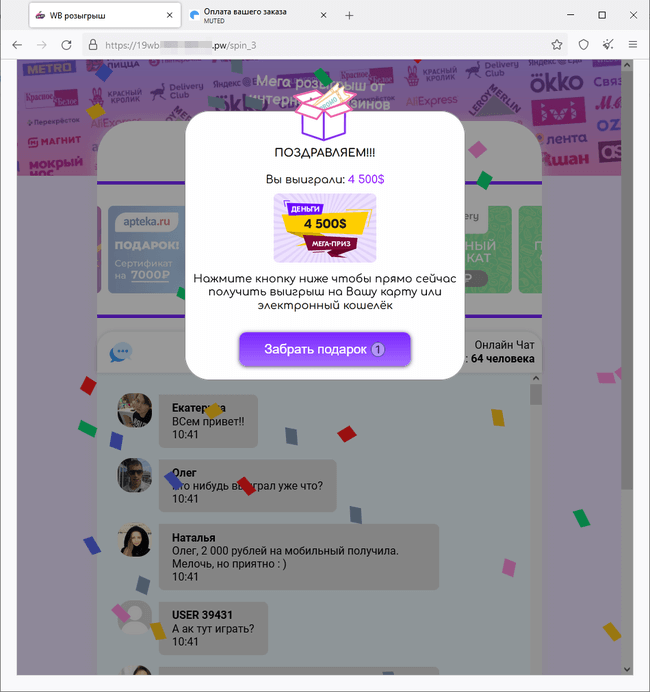
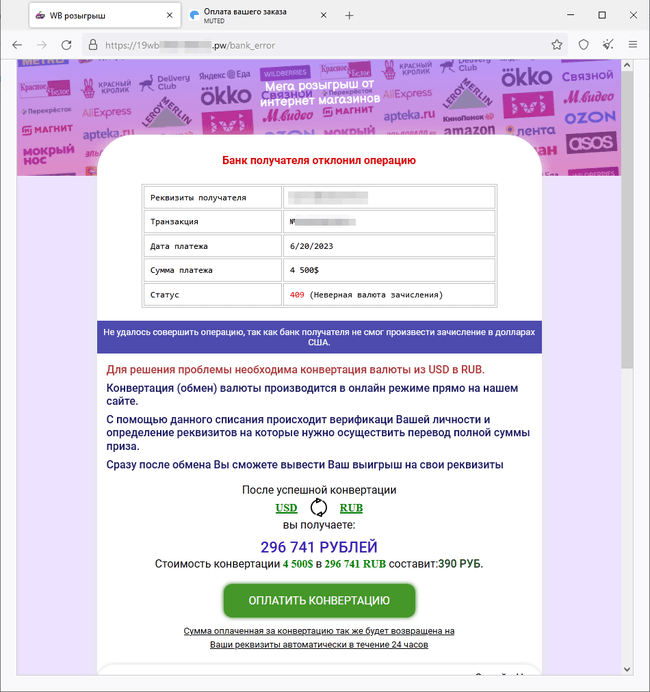
In addition, malicious actors continued creating fraudulent sites where visitors were invited to take part in prize and gift draws that had allegedly been organized on behalf of online stores. Potential victims were granted with several attempts. At first, they were “winning” freely available promo codes for a variety of services. However, the main “prize” would be a large cash reward in foreign currency. To get the money, users supposedly had to either pay a commission for the money to be transferred to their bank card or online wallet, or pay for the currency conversion. In reality though, victims of these fraudsters did not receive any of the promised cash prizes and rewards.
The screenshots above show an example of one of the fraudulent websites offering the opportunity to take part in prize “draws”. Based on a predetermined script, the site announces a win of $4,500. When the potential victim tries to obtain the prize, they see a message stating that an error has occurred and that they need to pay a commission to convert the currency into Russian rubles.
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
According to detection statistics collected by Dr.Web for Android, in June 2023, the activity of adware trojans from the Android.MobiDash family decreased. At the same time, users were more often attacked by a similar trojan family, Android.HiddenAds. Compared to May, Android device owners encountered spyware trojans and banking malware less often. By contrast, the number of Android.Locker ransomware trojan attacks increased.
Over the course of June, many new threats were detected on Google Play. Among them were malicious apps from the Android.FakeApp family and Android.Joker trojans that subscribe victims to paid services.
The following June events involving mobile malware are the most noteworthy:
- Adware trojans remain among the most widespread Android threats.
- A decrease in the activity of spyware trojans and banking malware.
- An increase in the activity of ransomware trojans.
- The emergence of new threats on Google Play.
To find out more about the security-threat landscape for mobile devices in June, read our special overview.
[% END %]