Doctor Web: Trojan Android.InfectionAds exploits critical vulnerabilities of Android to infect and install other software
Real-time threat news | Hot news | Threats to mobile devices | All the news
April 12, 2019
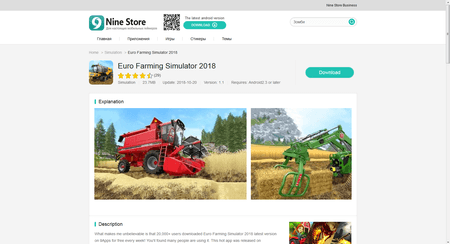
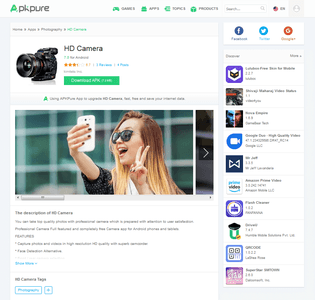
The attackers embed the trojan in initially harmless software and then distribute the modified copies via popular third-party Android stores, such as Nine Store and Apkpure. Our experts detected Android.InfectionAds.1 in games and software such as HD Camera, ORG 2018_19\Tabla Piano Guitar Robab Guitar, Euro Farming Simulator 2018, and Touch on Girls. Some of them were installed by at least several thousand mobile device owners. However, the number of infected applications and affected users may be much greater.
When a user launches a program containing a trojan, it extracts auxiliary modules from file resources to decrypt and launch them as well. One of them is designed to display obnoxious ads, while others infect applications and automatically install software.
Android.InfectionAds.1 overlays advertising banners on the system interface and running applications, making it difficult to work with the devices. In addition, if triggered by the command and control server, the trojan can modify the code of popular advertising platforms, such as Admob, Facebook, and Mopub, which are used in many programs and games. It replaces their advertising identifiers with its own identifier so that all profits from displaying advertisements in infected applications are transferred to the attackers.
Android.InfectionAds.1 exploits the critical vulnerability CVE-2017-13315 in Android, which allows the trojan to launch system activities. As a result, it can automatically install and uninstall programs without a user’s knowledge. The trojan is based on the PoC code (Proof of Concept) by Chinese researchers, written to prove the possibility of exploiting this system breach.
CVE-2017-13315 falls under the EvilParcel class of vulnerabilities. This means that a number of system components contain an error that allows for alteration of data during the exchange between applications and the operating system. The final value of the specifically generated fragment of the transmitted data will differ from the initial one. Thus, programs are able to bypass operating system checks, obtain higher privileges, and perform previously unavailable actions. As of now, we know of 7 vulnerabilities of this type, but the number may increase over time.
Using EvilParcel, Android.InfectionAds.1 installs the hidden APK file that contains all components of the trojan. Similarly, Android.InfectionAds.1 is able to install its own updates, downloaded from the command and control server, as well as other software or malware. For example, during our analysis, the trojan downloaded and installed the malware Android.InfectionAds.4, one of its own modifications.
An example of how the trojan installs applications without the user’s permission:
Along with EvilParcel, the trojan also exploits another Android vulnerability known as Janus (CVE-2017-13156). This system breach can be used to infect previously installed applications by embedding the trojan’s copy within them. Android.InfectionAds.1 connects to the command and control server and obtains a list of programs that it needs to infect. If it fails to connect to the remote server, it will infect applications specified in the initial settings. Depending on the modification, the list may contain different items. See below an example from one of the versions of Android.InfectionAds.1 we have investigated:
- com.whatsapp (WhatsApp Messenger);
- com.lenovo.anyshare.gps (SHAREit - Transfer & Share);
- com.mxtech.videoplayer.ad (MX Player);
- com.jio.jioplay.tv (JioTV - Live TV & Catch-Up);
- com.jio.media.jiobeats (JioSaavn Music & Radio – including JioMusic);
- com.jiochat.jiochatapp (JioChat: HD Video Call);
- com.jio.join (Jio4GVoice);
- com.good.gamecollection;
- com.opera.mini.native (Opera Mini - fast web browser);
- in.startv.hotstar (Hotstar);
- com.meitu.beautyplusme (PlusMe Camera - Previously BeautyPlus Me);
- com.domobile.applock (AppLock);
- com.touchtype.swiftkey (SwiftKey Keyboard);
- com.flipkart.android (Flipkart Online Shopping App);
- cn.xender (Share Music & Transfer Files – Xender);
- com.eterno (Dailyhunt (Newshunt) - Latest News, LIVE Cricket);
- com.truecaller (Truecaller: Caller ID, spam blocking & call record);
- com.ludo.king (Ludo King™).
To infect software, the trojan embeds its components in APK files without changing the digital signature. Then it installs the modified versions of the apps instead of the originals. Since the vulnerability helps the digital signature of the infected files remain the same, the programs are installed as their own updates. At the same time, EvilParcel helps perform the installation independently from the user. As a result, the affected software continues its normal operations, but with a functioning copy of Android.InfectionAds.1 within it. Once apps are infected, the trojan gets access to their data. For example, if WhatsApp is infected, the trojan gets access to all users’ messages, if a browser is infected, saved logins and passwords are available to the trojan.
The only way to remove the trojan and restore the security of the infected programs is to remove the applications containing it and reinstall their normal versions from reliable sources, such as Google Play. The updated version of Dr.Web Security Space for Android is able to detect EvilParcel vulnerabilities. This feature is available in Security Auditor. You can download a new distribution package from the Doctor Web official website. Soon it will be available on Google Play as well. All Dr. Web products for Android successfully detect and remove known modifications of Android.InfectionAds.1, so the trojan does not pose any threat to our users.
[Read more about Android.InfectionAds.1]
#Android, #trojan, #malware