January 2018 virus activity review from Doctor Web
January 31, 2018
The beginning of 2018 was marked by the detection of several Android games on Google Play that contained an embedded Trojan. This Trojan downloaded and launched malicious modules on infected devices. Virus analysts also examined several miner Trojans that infected Windows servers. They all used a vulnerability in the software Cleverence Mobile SMARTS Server.
Principal trends in January
- The detection of a dangerous Android Trojan on Google Play
- Distribution of new versions of miner Trojans that infect Windows servers
Threat of the month
The Cleverence Mobile SMARTS Server is a complex of applications for automizing shops, warehouses, various facilities and productions. Doctor Web analysts detected a 0-day vulnerability in these programs back in July 2017 and informed software developers about it. Soon they released a security update for their product. However, by no means had all administrators installed these updates, which left cybercriminals the possibility to continue hacking vulnerable servers. For this purpose, cybercriminals send a special request to a vulnerable server, which results in executing the command contained in this request. The attackers created a new user with administrator privileges in the system and employed this user account to get unauthorized access to the server via the RDP protocol. In some cases, cybercriminals use the Process Hacker tool to shut down the processes of anti-viruses running on the server. Once they obtain access to the system, they install the Trojan miner on it.
The miner used by the cybercriminals is constantly updated. Initially, they used several Trojan modifications added to the Doctor Web virus database as Trojan.BtcMine.1324, Trojan.BtcMine.1369 and Trojan.BtcMine.1404. Later this list was updated with Trojan.BtcMine.2024, Trojan.BtcMine.2025, Trojan.BtcMine.2033, and the most up-to-date version is Trojan.BtcMine.1978.
The Trojan is launched as a critically important process. If one tries to shut down this process, Windows performs an emergency shutdown and displays the “blue screen of death” (BSOD). After it is launched, the miner attempts to shut down processes and delete the services of several anti-viruses. Cybercriminals use Trojan.BtcMine.1978 to mine cryptocurrencies Monero (XMR) and Aeon. Dr.Web specialists recommend that all security updates for the Cleverence Mobile SMARTS Server released by the developers be installed. For more information about this incident, refer to the review published on our website.
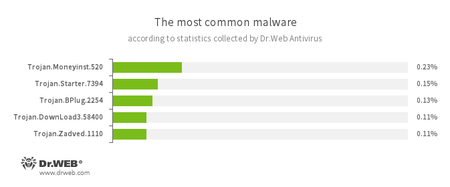
According to Dr.Web Anti-virus statistics
- Trojan.Moneyinst.520
- A malicious program that installs various software, including other Trojans, on a victim's computer.
- Trojan.Starter.7394
- A Trojan whose main purpose is to launch in an infected system with an executable file possessing a specific set of malicious functions.
- Trojan.BPlug
- These plug-ins for popular browsers display annoying advertisements to users browsing webpages.
- Trojan.DownLoad
- A family of malicious programs designed to download other malware to the compromised computer.
- Trojan.Zadved
- This Trojan displays fake search results in the browser window and imitates pop-up messages from social networking sites. In addition to this, the malware can replace advertisements displayed on different Internet resources.
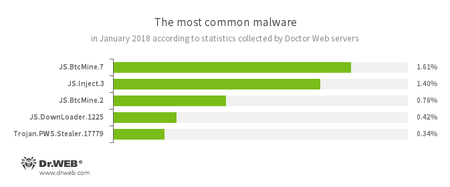
According to Doctor Web’s statistics servers
- JS.BtcMine.7, JS.BtcMine.2
- A JavaScript designed to stealthily mine cryptocurrencies (mining).
- JS.Inject
- A family of malicious JavaScripts. They inject a malicious script into the HTML code of web pages.
- JS.DownLoader
- A family of malicious JavaScripts. They download and install malicious software on a computer.
- Trojan.PWS.Stealer
- A family of Trojans designed to steal passwords and other confidential information stored on an infected computer.
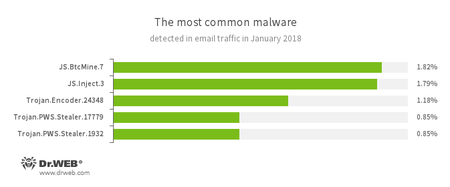
Statistics concerning malicious programs discovered in email traffic
- JS.BtcMine.7
- A JavaScript designed to stealthily mine cryptocurrencies (mining).
- JS.Inject
- A family of malicious JavaScripts. They inject malicious script into the HTML code of webpages.
- Trojan.Encoder.24348
- A malicious program belonging to the family of encryption ransomware Trojans that encrypt files and demand a ransom to decrypt compromised data.
- Trojan.PWS.Stealer
- A family of Trojans designed to steal passwords and other confidential information stored on an infected computer.
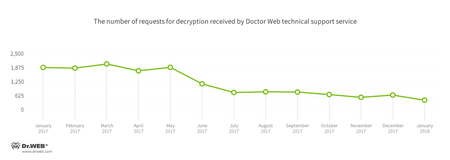
Encryption ransomware
In January, Doctor Web’s technical support was most often contacted by victims of the following modifications of encryption ransomware:
- Trojan.Encoder.858 — 22.12% of requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.567 — 7.83% of requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.11539 — 6.45% of requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.2267 — 3.46% of requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.761 — 3.23% of requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.3953 — 3.20% of requests.
Dr.Web Security Space for Windows protects against encryption ransomware
Dangerous websites
During January 2018, 309,933 URLs of non-recommended websites were added to the Dr.Web database.
| December 2017 | January 2018 | Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| + 241,274 | + 309,933 | +28.4% |
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
In January, Doctor Web virus analysts found Android.RemoteCode.127.origin embedded in numerous Android games available on Google Play. It covertly downloaded and launched malicious modules that performed various actions. Additionally, over the past month, a banking Trojan Android.BankBot.250.origin posed a threat to users. It stole login credentials to access online banking accounts. In January, security specialists also detected a malicious mining program dubbed Android.CoinMine.8. This Trojan used the computing power of infected smartphones and tablets to mine the Monero cryptocurrency. Also in January, the Dr.Web virus database was updated with several entries for detecting Android spyware. One of them was Android.Spy.422.origin. Other malicious applications were new modifications of Android.Spy.410.origin which was spread back in December 2017.
Among the most notable January events related to mobile malware we can report the following:
- The detecting of a new Trojan on Google Play;
- The spreading of a new Android miner that used infected mobile devices to mine cryptocurrency;
- The detection of new spyware Trojans.
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.