Android backdoor spies on employees of Russian businesses
Real-time threat news | Hot news | Threats to mobile devices | All the news
August 20, 2025
The first Android.Backdoor.916.origin versions emerged in January 2025. Since discovering the backdoor, Doctor Web’s anti-virus laboratory has tracked the malware’s evolution and detected a number of versions (information about them is provided in the corresponding indicators of compromise) of it. Our experts believe that Android.Backdoor.916.origin is likely designed more for targeted attacks than for mass distribution among Android device users. Its main target is Russian business representatives.
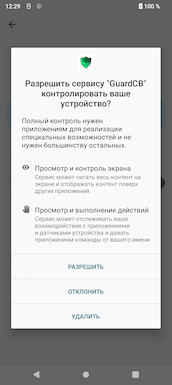
Threat actors use direct messages in messengers to distribute the backdoor’s APK file under the guise of an anti-virus called “GuardCB”. The app’s icon resembles the emblem of the Russian Federation’s Central Bank; the emblem is set against the background of a shield. At the same time, the app’s interface provides only one language—Russian. Thus, the malware is entirely focused on Russian users. This is confirmed by other detected modifications with names like “SECURITY_FSB”, “ФСБ” (FSB), and others, which cybercriminals are trying to pass off as security-related programs that are supposedly related to Russian law enforcement agencies.
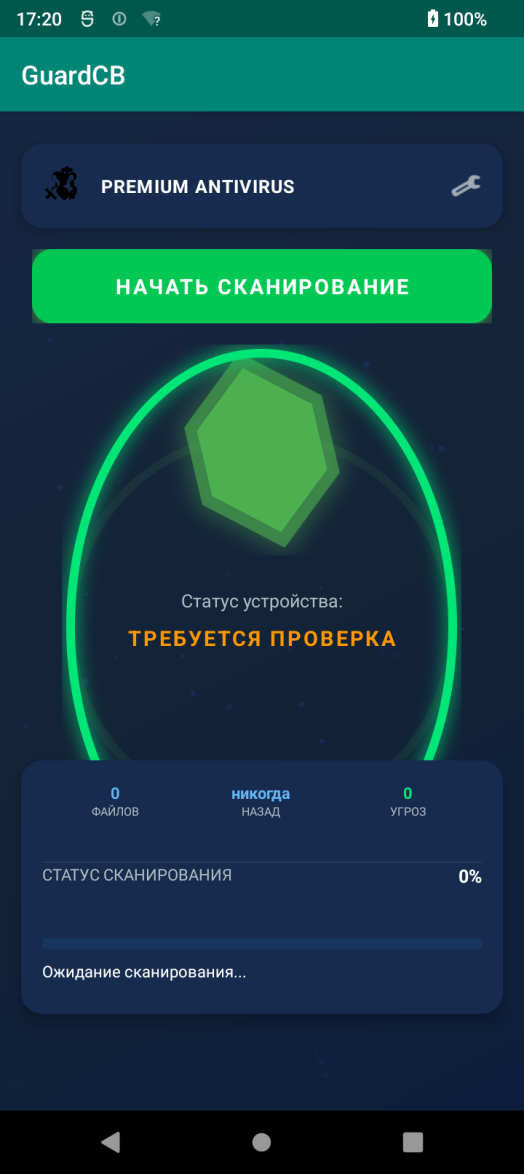
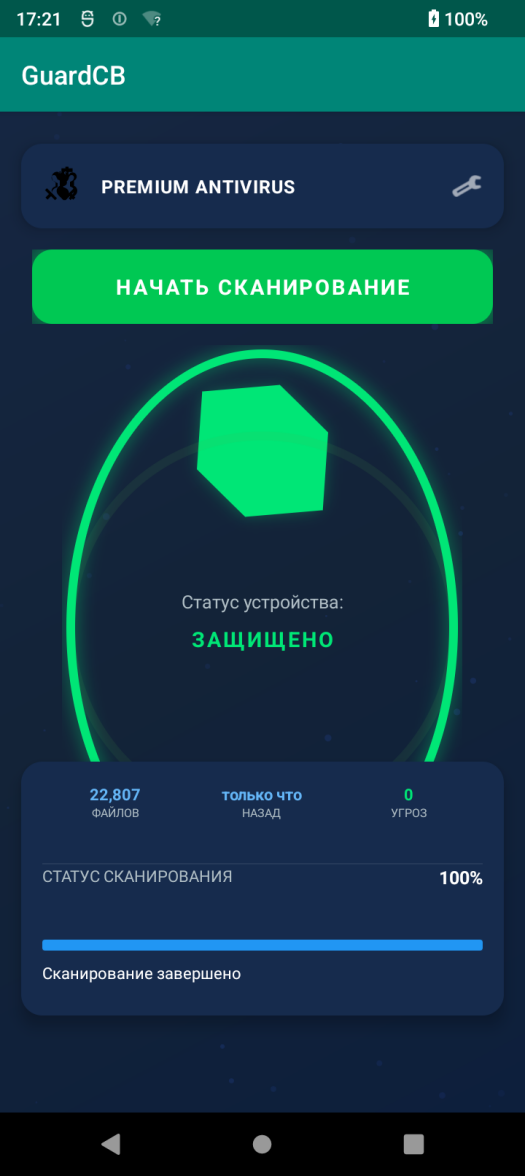
Icons of the malware mislead potential victims
The app does not in fact have any anti-virus features. When it runs, Android.Backdoor.916.origin acts like it is performing an anti-virus scan on a device, while the probability of “detecting” threats is programmed into it. The more time that has passed since the previous “scan”, the higher the chance is, but no more than 30%. The number of allegedly found threats is determined randomly and ranges from 1 to 3.
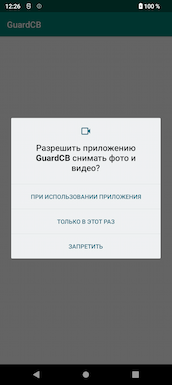
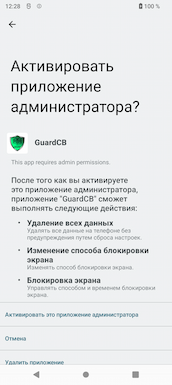
When it first launches, Android.Backdoor.916.origin requests access to many system permissions:
- Geolocation;
- Audio recording;
- Access to SMS, contacts, call history, media files, permission to make calls;
- Camera (to take pictures and record videos);
- Permission to run in the background;
- Device administrator rights;
- Accessibility Service.
Examples of the requested permissions
The malware then launches several of its own services and checks their activity every minute, restarting them again if needed. The backdoor uses these services to connect to the C2 server and receive a large number of commands. Among them are:
- upload incoming and outgoing SMS to the C2 server;
- upload the contacts list to the C2 server;
- upload call history to the C2 server;
- upload geolocation data to the C2 server;
- start or stop audio streaming through the device’s microphone;
- start or stop video streaming from the device’s camera;
- start or stop streaming the device’s screen;
- upload all images stored on a memory card to the C2 server;
- upload images from a memory card to the C2 server according to a given range of names;
- upload a specified image from a memory card to the C2 server;
- enable or disable the backdoor’s self-protection;
- execute a received shell command;
- upload information about the device’s network and interfaces to the C2 server.
The backdoor streams the different types of data it collects to separate C2 server ports.
Android.Backdoor.916.origin uses Accessibility Service to execute keylogger functionality and intercept content from messengers and browsers. These apps are monitored by the trojan:
- Telegram
- Google Chrome
- Gmail
- Яндекс Старт (Yandex Start)
- Яндекс Браузер (Yandex Browser)
The backdoor also uses Accessibility Service to protect itself from being deleted if it receives the corresponding command from the threat actors.
Android.Backdoor.916.origin has functionality that allows it to operate with a large number of C2 servers whose information is stored in its configuration. Moreover, it can switch between hosting providers, the number of which can be as high as 15, but this option is not being used at the moment. Doctor Web’s anti-virus laboratory has informed domain registrars about the violations it has uncovered.
Dr.Web Security Space for mobile devices reliably detects and removes all known Android.Backdoor.916.origin modifications, keeping our users well protected from this threat.
More about Android.Backdoor.916.origin