Doctor Web’s July 2023 virus activity review
September 15, 2023
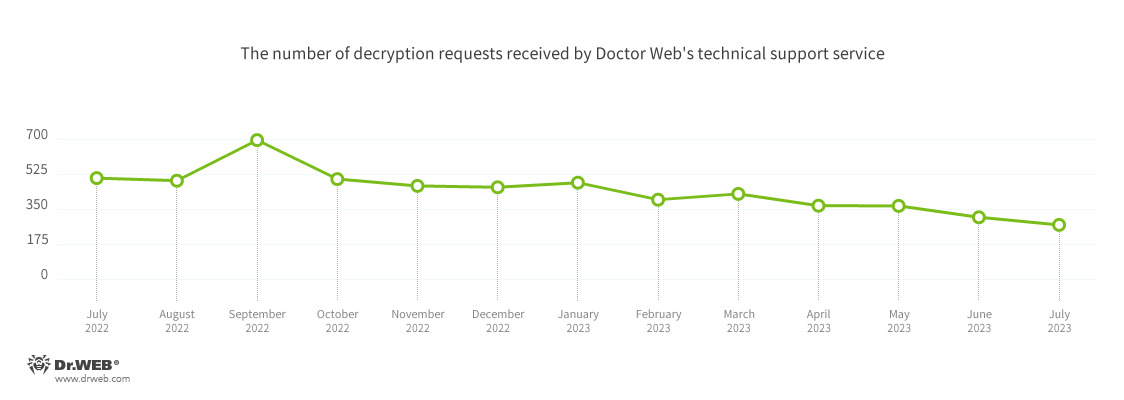
The number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoder trojans decreased by 12.30%, compared to June. The most common encoder was Trojan.Encoder.26996, with a share of 21.61% of all incidents recorded. The second most widespread encoder again was Trojan.Encoder.3953, which accounted for 19.10% of all requests. Third place was taken by Trojan.Encoder.35534, with a share of 3.52%.
New malicious programs were spotted on Google Play in July. Among them were trojans from the Android.Joker and Android.Harly families that subscribe victims to paid services, and a crypto-stealing trojan.
Principal trends in July
- A decrease in the total number of detected threats
- A decrease in the number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoder trojans
- The distribution of new malware on Google Play
According to Doctor Web’s statistics service
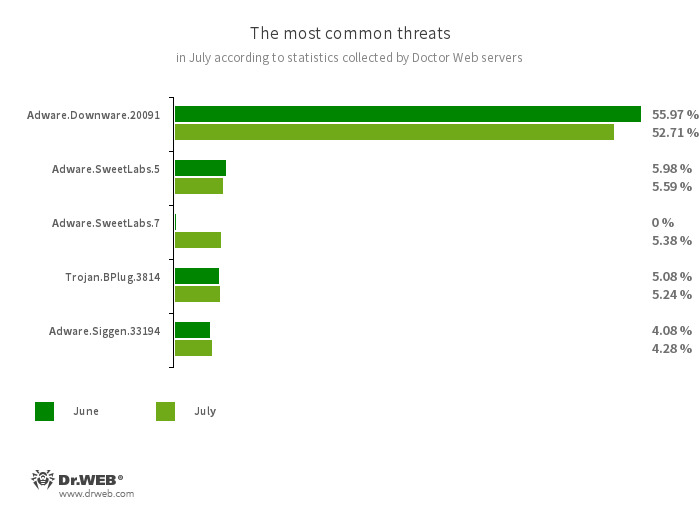
The most common threats in July:
- Adware.Downware.20091
- Adware that often serves as an intermediary installer of pirated software.
- Adware.SweetLabs.5
- Adware.SweetLabs.7
- An alternative app store and an add-on for Windows GUI (graphical user interface) from the creators of “OpenCandy” adware.
- Trojan.BPlug.3814
- The detection name for a malicious component of the WinSafe browser extension. This component is a JavaScript file that displays intrusive ads in browsers.
- Adware.Siggen.33194
- The detection name for a freeware browser that was created with an Electron framework and has a built-in adware component. This browser is distributed via various websites and loaded onto users’ computers when they try downloading torrent files.
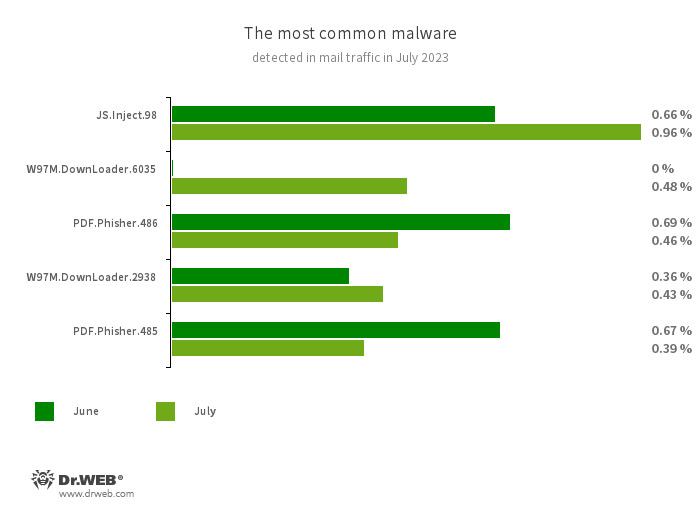
Statistics for malware discovered in email traffic
- JS.Inject
- A family of malicious JavaScripts that inject a malicious script into the HTML code of webpages.
- W97M.DownLoader.6035
- W97M.DownLoader.2938
- A family of downloader trojans that exploit vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office documents. They can also download other malicious programs to a compromised computer.
- PDF.Phisher.486
- PDF.Phisher.485
- PDF documents used in phishing newsletters.
Encryption ransomware
In July, the number of requests to decrypt files affected by encoder trojans decreased by 12.30%, compared to June.
The most common encoders of July:
- Trojan.Encoder.26996 — 21.61%
- Trojan.Encoder.3953 — 19.10%
- Trojan.Encoder.35534 — 3.52%
- Trojan.Encoder.35209 — 3.02%
- Trojan.Encoder.29750 — 2.51%
Dangerous websites
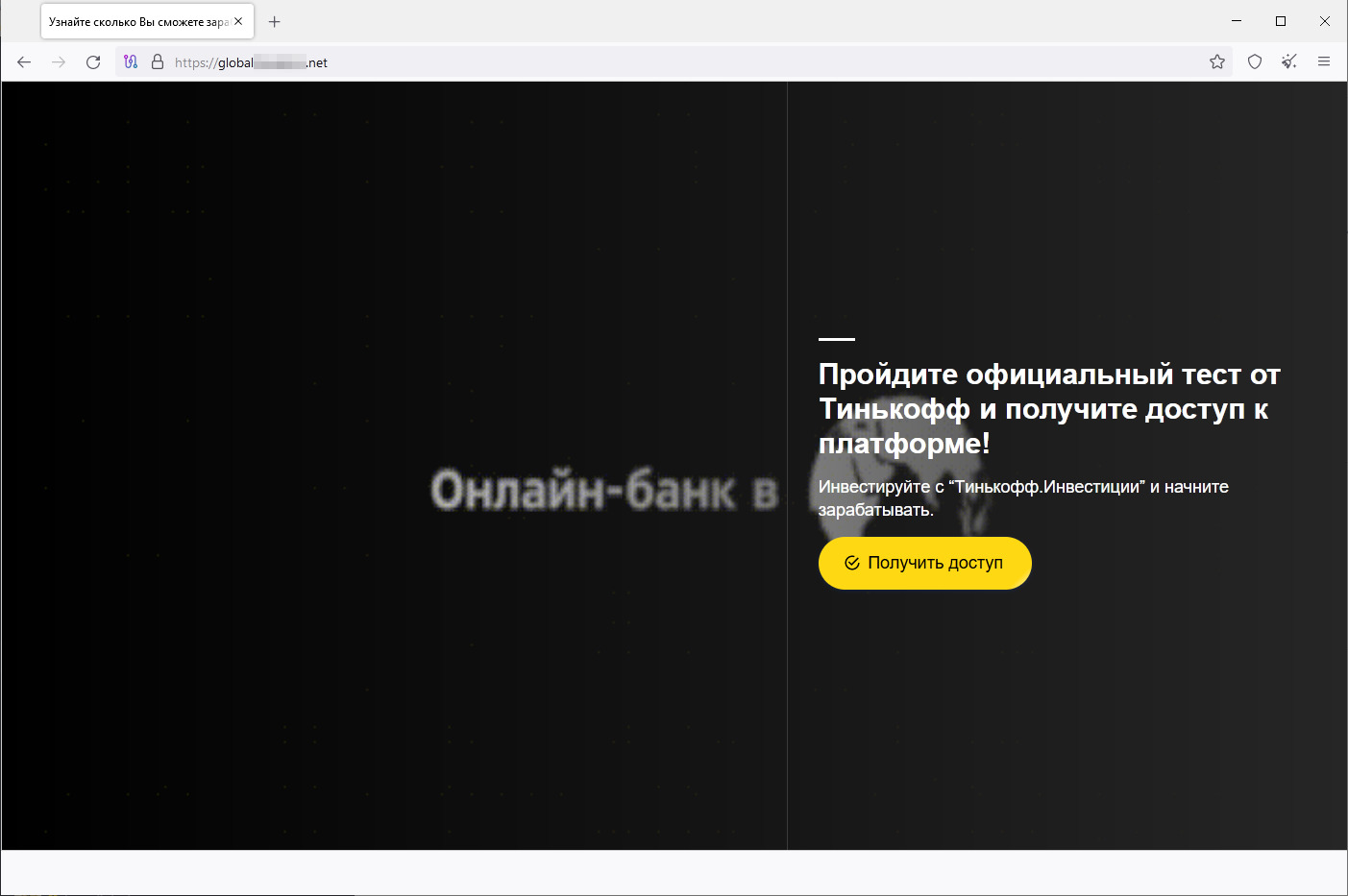
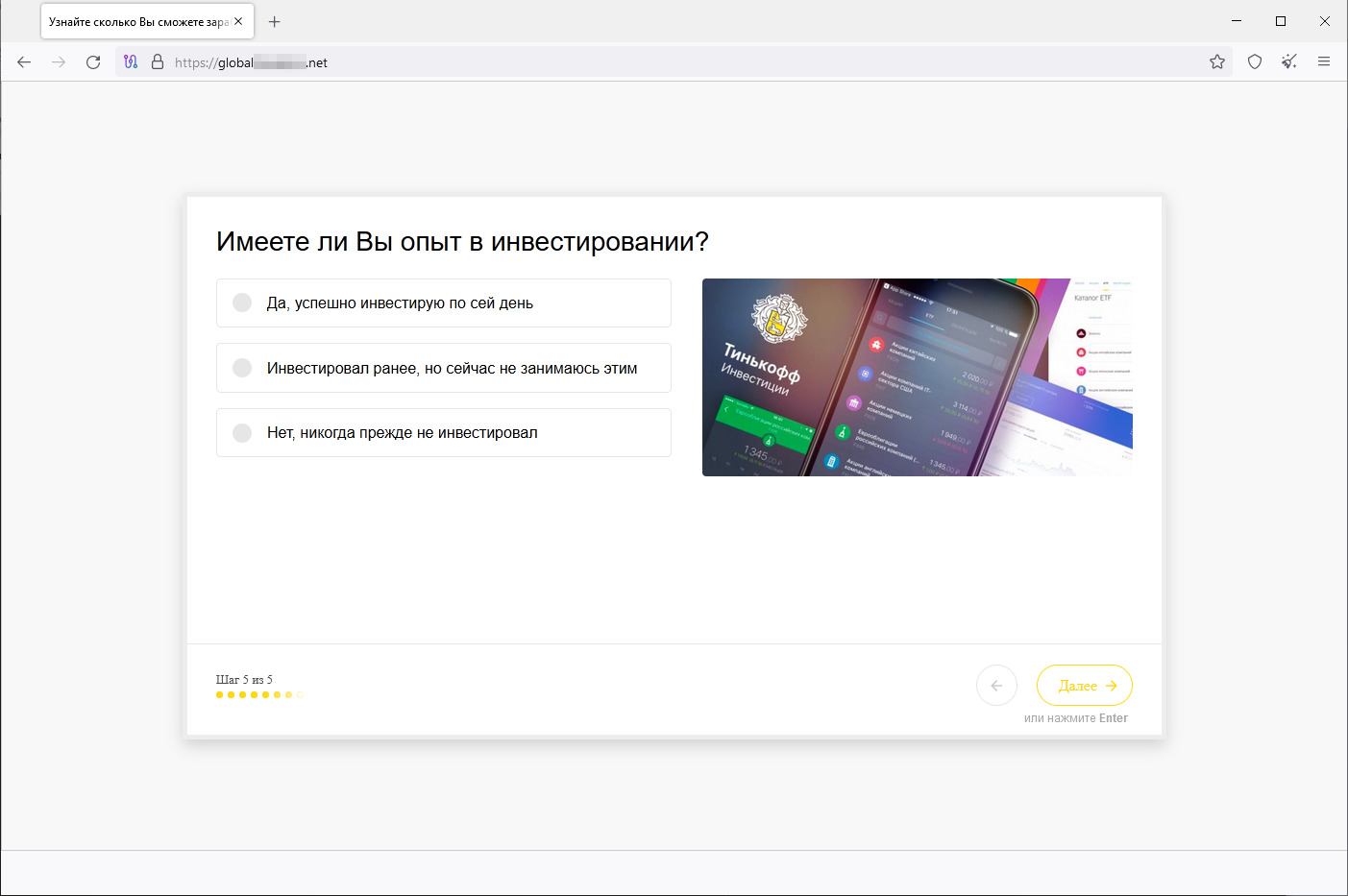
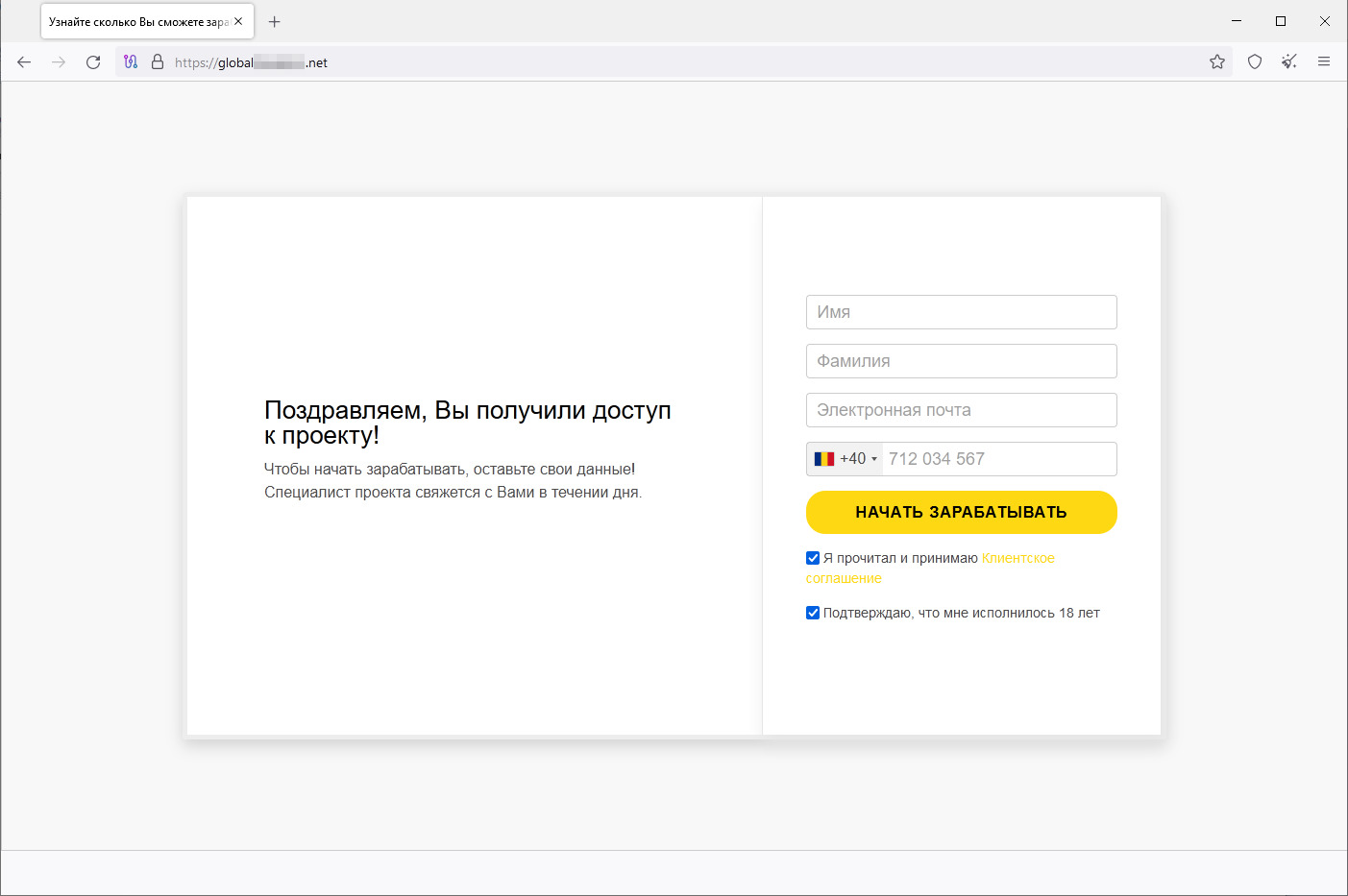
In July, users again encountered various phishing websites that are allegedly associated with banks, oil and gas, and other companies and invite visitors to become investors. Potential victims are asked to provide personal information and then to wait for an “expert” to call them back. The data entered on such resources is sent to third parties and can later be used for fraudulent purposes. Below are the screenshots of one such site.
The visitor is asked to take a test in order to access the “investing platform”:
Next, they are asked to provide personal information, such as their first and last names, email address, and phone number:
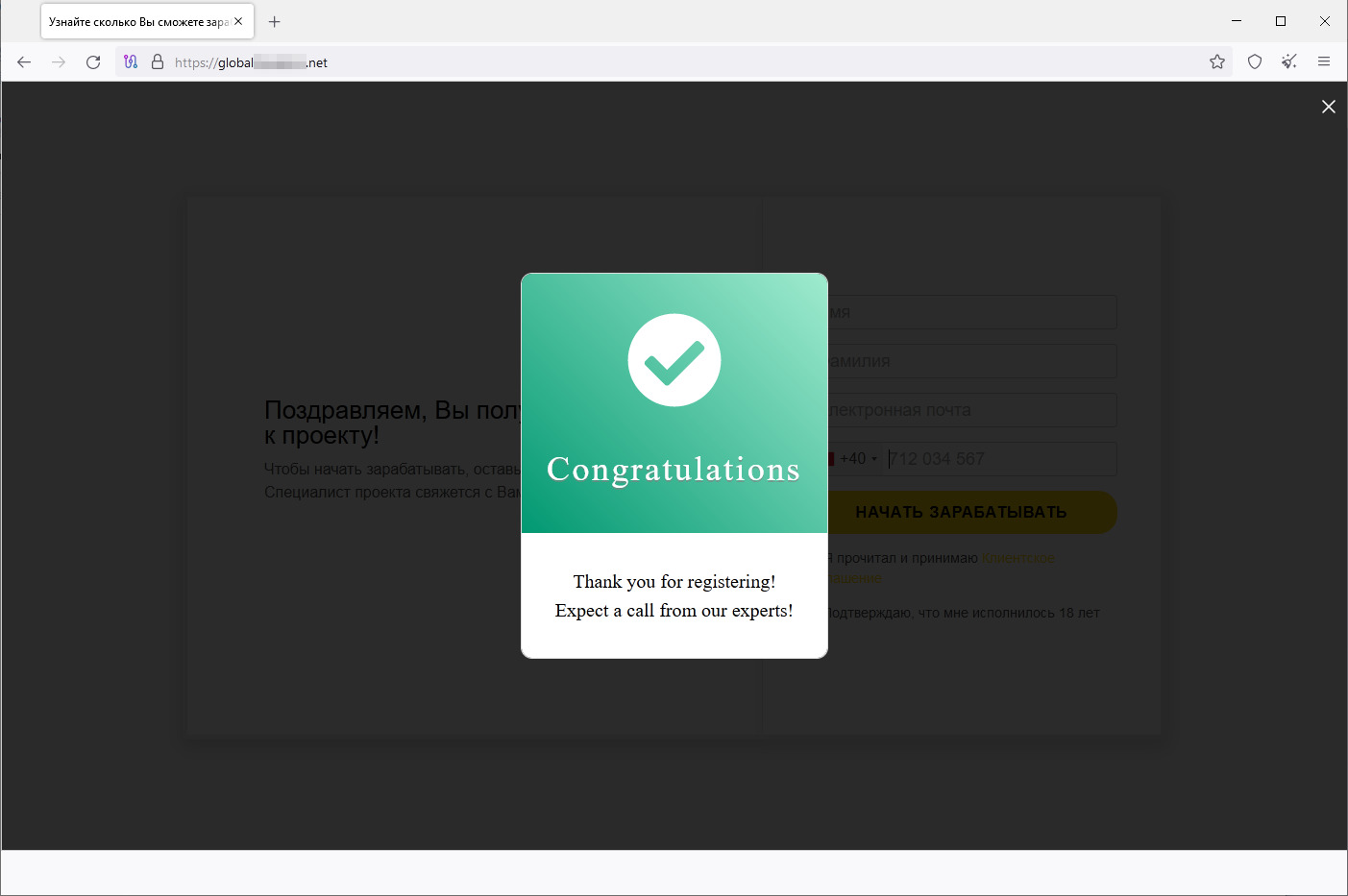
When the user confirms the input, the site informs them that their “registration” was successful and that they need to wait for an “expert” to call them.
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
According to detection statistics collected by Dr.Web for Android, in July 2023, users encountered Android.HiddenAds adware trojans more often. At the same time, the activity of adware trojans from the Android.MobiDash family decreased. The activity of ransomware and banking malware increased, compared to June. Meanwhile, Android device owners were attacked by spyware trojans less often.
Over the course of July, new threats were detected on Google Play. Among them were the Android.Harly.80, Android.Joker.2170, Android.Joker.2171, and Android.Joker.2176 trojan apps, which subscribed victims to paid services. In addition, our specialists discovered Android.CoinSteal.105—a crypto-stealing trojan.
The following July events involving mobile malware are the most noteworthy:
- An increase in the activity of Android.HiddenAds adware trojans,
- A decrease in the activity of Android.MobiDash adware trojans,
- An increase in the activity of banking malware and ransomware trojans,
- The distribution of new threats on Google Play.
To find out more about the security-threat landscape for mobile devices in July, read our special overview.