February 28, 2018
In February, a ransomware Trojan was spread. This Trojan infects computers running Microsoft Windows. It appends the extension *.GDCB to encrypted files. The final winter month is also marked by the emergence of a miner Trojan for Android. This Trojan can distribute itself on its own, infecting network devices by enabled debugging mode. Smartphones, tablets, media players, routers and “smart” TVs can be infected by the Trojan.
Principal trends in February
- The distribution of a new encoder for Windows
- The emergence of a miner Trojan for Android
Threat of the month
Doctor Web security researchers detected a ransomware Trojan, Trojan.Encoder.24384. This Trojan is also known as “GandCrab!”, given to this Trojan by cybercriminals. The Trojan encrypts the contents of the fixed, removable and network disks. It also appends the extension *.GDCB to encrypted files. Once launched, under certain circumstances, the encoder checks for anti-virus programs on the infected computer. The Trojan then closes some running programs and installs itself on the system. The programs are specified by cybercriminals.
After restarting the computer, Trojan.Encoder.24384 encrypts files on the disk, except for system directories. We discuss this malicious program’s operating routines in our overview.
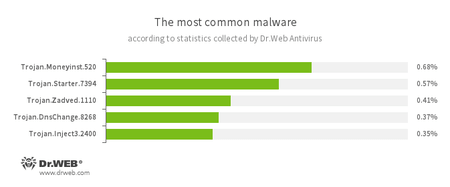
According to Dr.Web Anti-virus statistics
- Trojan.Moneyinst.520
- A malicious program that installs various software, including other Trojans, on a victim's computer.
- Trojan.Starter.7394
- A Trojan whose main purpose is to launch in an infected system with an executable file possessing a specific set of malicious functions.
- Trojan.Zadved
- This Trojan displays fake search results in a browser window and imitates pop-up messages from social networking sites. In addition, the malware can replace advertisements displayed on different Internet resources.
- Trojan.DnsChange.8268
- A malicious program that modifies DNS servers’ addresses on the infected device.
- Trojan.Inject
- A family of malicious programs that inject malicious code into the processes of other programs.
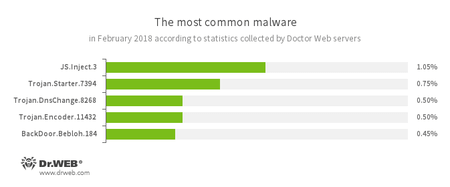
According to Doctor Web’s statistics servers
- JS.Inject
- A family of malicious JavaScripts that inject a malicious script into the HTML code of webpages.
- Trojan.Starter.7394
- A Trojan whose main purpose is to launch in an infected system with an executable file possessing a specific set of malicious functions.
- Trojan.DnsChange.8268
- A malicious program that modifies DNS servers’ addresses on the infected device.
- Trojan.Encoder.11432
- A network worm that launches a dangerous ransomware Trojan on a victim’s computer. This Trojan is also known as ‘WannaCry’.
- BackDoor.Bebloh
- A malicious program belonging to the family of banking Trojans. This application poses a threat to users of e-banking services (RBS), because it allows cybercriminals to steal confidential information by intercepting data submitted through forms in the browser window and by embedding the malicious code into bank webpages.
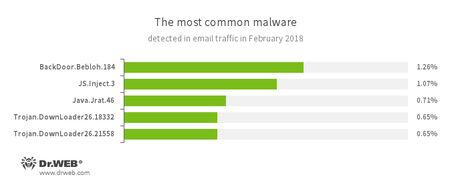
Statistics concerning malicious programs discovered in email traffic
- BackDoor.Bebloh
- A malicious program belonging to the family of banking Trojans. This application poses a threat to users of e-banking services (RBS), because it allows cybercriminals to steal confidential information by intercepting data submitted through forms in the browser window and by embedding the malicious code into bank webpages.
- JS.Inject
- A family of malicious JavaScripts that inject a malicious script into the HTML code of webpages.
- Java.Jrat.46
- Malware that controls computers remotely (Remote Access Tools, RAT). This malicious program is written in Java.
- Trojan.DownLoader
- A family of malicious programs designed to download other malware to the compromised computer.
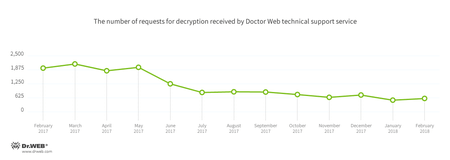
Encryption ransomware
In February, Doctor Web’s technical support was most often contacted by victims of the following modifications of encryption ransomware:
- Trojan.Encoder.858 — 24.33% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.567 — 8.25% of requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.24249 — 6.19% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.11539 — 3.92% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.11464 — 2.68% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.2667 — 2.67% requests.
Dr.Web Security Space for Windows protects against encryption ransomware
Dangerous websites
During February 2018, the number of URLs of non-recommended websites added to the Dr.Web database was 278.9% higher than in the previous month.
| January 2018 | February 2018 | Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| + 309,933 | + 1,174,380 | +278.9% |
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
In February, security specialists detected a miner Trojan, Android.CoinMine.15. The Trojan can remotely infect Android smartphones, tablets, TVs, routers, and media players connected to the network. The infection is possible only when the devices have the debugging mode enabled. Once the infection has been completed, the malicious program attempts to detect other devices connected to the network and installs its copy on them. Additionally, in the past month, cybercriminals distributed a banking Trojan via Google Play. The Trojan is detected as Android.BankBot.336.origin. This banking Trojan steals confidential information and money from users.
Among the most noticeable February events related to mobile malware were:
- The detection of a miner Trojan that infects Android devices connected to the network;
- The distribution of a new banking Trojan.
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.