Doctor Web discovers Trojan installing unwanted software and unremovable ads
Real-time threat news | Hot news | All the news | Virus alerts
December 16, 2016
Trojan.Ticno.1537 is downloaded onto a computer by another malware program. Once launched, the Trojan searches for the virtual environment and debugging tools by checking the names of the running processes and the corresponding branches of the Windows system registry. In addition, Trojan.Ticno.1537 verifies the Product ID, user and computer names, the number of nested folders in Program Files, the name of the BIOS producer, and it discerns whether the running processes, perl.exe or python.exe, are present. If the scanning process is successful, the Trojan launches the Explorer and terminates its operation.
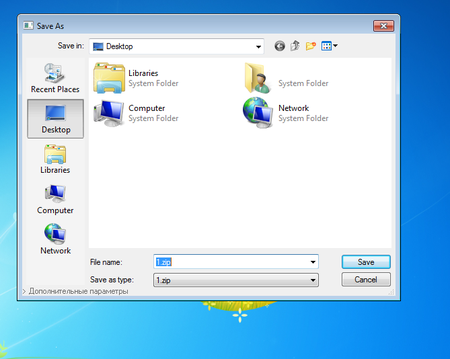
If the Trojan does not find anything suspicious, it saves the file 1.zip on the disk.
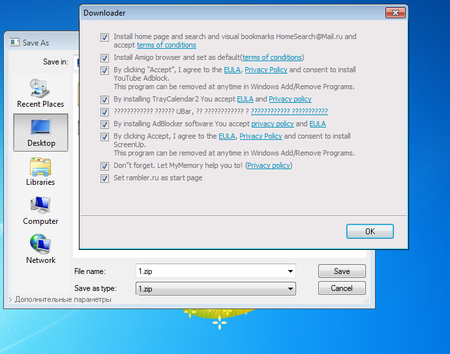
The picture above shows a non-standard Microsoft Windows “save” dialog box: in the bottom-left corner, you can see the link “Additional settings”. When the link is clicked, Trojan.Ticno.1537 displays the list of programs it is ready to install on the computer:
If the user clicks “Save”, Trojan.Ticno.1537 downloads and installs these programs.
Among the applications Trojan.Ticno.1537 installs on the victim’s computer are the browser Amigo and the program HomeSearch@Mail.ru (developed by Mail.Ru) and the Trojans Trojan.ChromePatch.1, Trojan.Ticno.1548, Trojan.BPlug.1590, Trojan.Triosir.718, Trojan.Clickmein.1, and Adware.Plugin.1400.
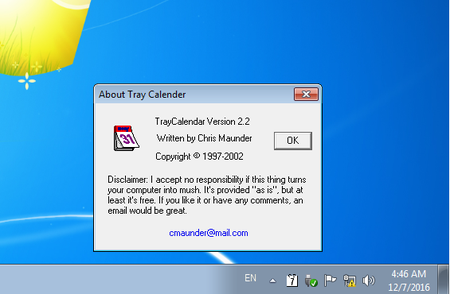
The above-mentioned Trojan.ChromePatch.1 is an adware program that is distributed via the application TrayCalendar, which was created in 2002. The program and the Trojan are packed in a single installation package.
While TrayCalendar is being copied to the disk, the Trojan saves and installs an extension for Google Chrome. The most notable feature of Trojan.ChromePatch.1 is that it infects the Chrome resource file—resources.pak. Cybercriminals have been using this method since at least spring 2015 to force the display of advertisements even after the Trojan has been removed from a computer. The size of this file remains unchanged during the infection process because Trojan.ChromePatch.1 searches it for strings containing comments and replaces them with its code. Trojan.ChromePatch.1 is designed to show advertisements in the Chrome browser.
Dr.Web Anti-virus successfully detects and removes all the Trojans mentioned above. Therefore, they do not pose any threat to our users.